Webinar on Child Migrants in Family Immigration Detention: Examining Pediatric Care Standards and Policies
On Thursday, May 2, 2024 at 12:00pm – 1:00pm EDT, the FXB Center for Health and Human Rights at Harvard University will host a virtual conversation on the key findings…
Economic Growth Slows Down Despite Increased Labor Pool in US: The Impact on Interest Rates and Inflation
In recent years, the US economy has experienced strong growth, thanks to a variety of factors such as increased net migration flows. This has led to a larger labor pool,…
Montgomery County and City Join Forces to Boost Small Businesses with $2.5 Million Loan Program
Montgomery County and the City of Montgomery are joining forces to utilize funds from the American Rescue Plan to support small businesses in the region. Mayor Steven Reed highlighted the…
A1 Video: Snowy sledding with visibility under 100 meters in some areas
We were driving near Delnice towards Rijeka when we encountered harsh winter conditions. With temperatures at 0 degrees and a mix of sleet, snow, and fog, visibility was severely limited…
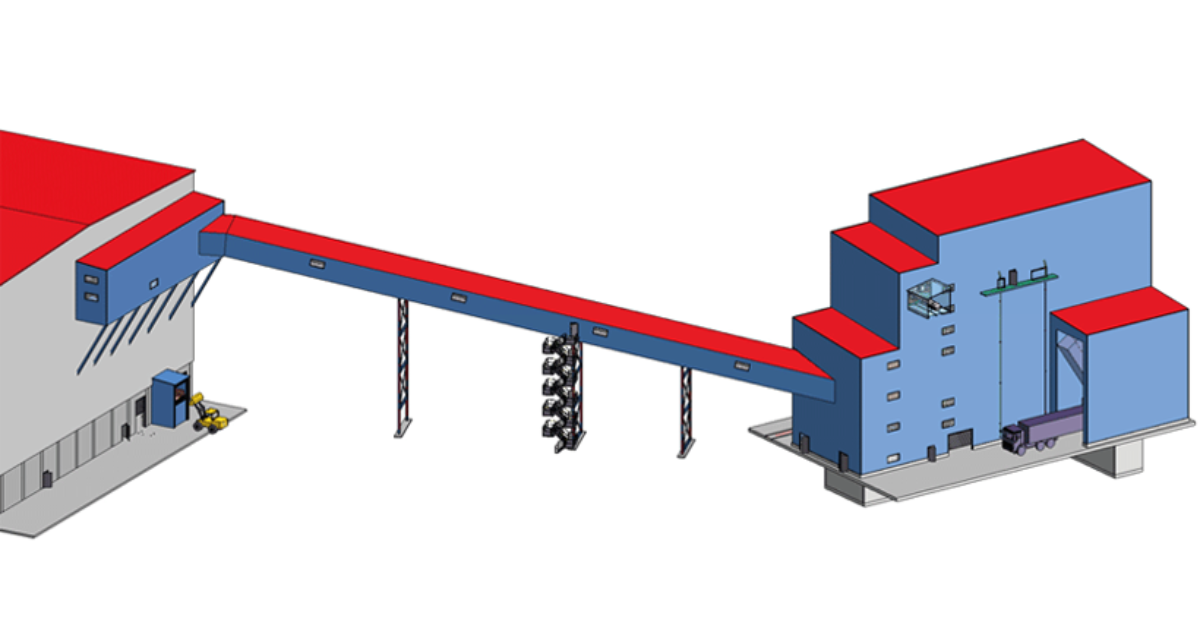
Arglass makes second investment in Zippe batch plant technology for glass production
Arglass and Zippe are teaming up for the construction of Arglass’s second plant in Valdosta, USA. The project is scheduled for installation in December 2024 and will be commissioned in…
Injured list for Rays closer Pete Fairbanks due to nerve-related issues
The Tampa Bay Rays made the decision to place struggling closer Pete Fairbanks on the 15-day injured list due to nerve-related issues before their game against the Detroit Tigers. Fairbanks…
New Fishery and Oceanographic Research Vessel to Replace 35-Year-Old Ship: AFBI Partners with Armon for Construction and Skipsteknisk for Design”.
The Agri-Food and Biosciences Institute (AFBI) in Belfast, Northern Ireland is set to embark on a major research project with the construction of a new vessel. This vessel will be…
Is Traditional Medicine for Thyroid Cancer the Right Choice? The Consequences of Opting Out of Surgery
Thuy Linh, a 35-year-old from An Giang, had thyroid cancer for a year but opted for traditional medicine instead of undergoing surgery. Recently, she has been experiencing a sore throat…
Greece’s Economy: A Positive Development in the European Economy, Says National Economy and Finance Minister Kostis Hatzidakis
Greece’s economy has been viewed as a positive development in the European economy, according to National Economy and Finance Minister Kostis Hatzidakis. During the Spring Meetings of the International Monetary…
Target’s Spring Grocery Collection: Your Ultimate Guide to Healthy Eating and Med diet Staples
This spring, I’m excited to explore Target’s exceptional home decor collection. Their sundress selection is always impressive, making it the perfect place to find pastel clothing for the season. But…