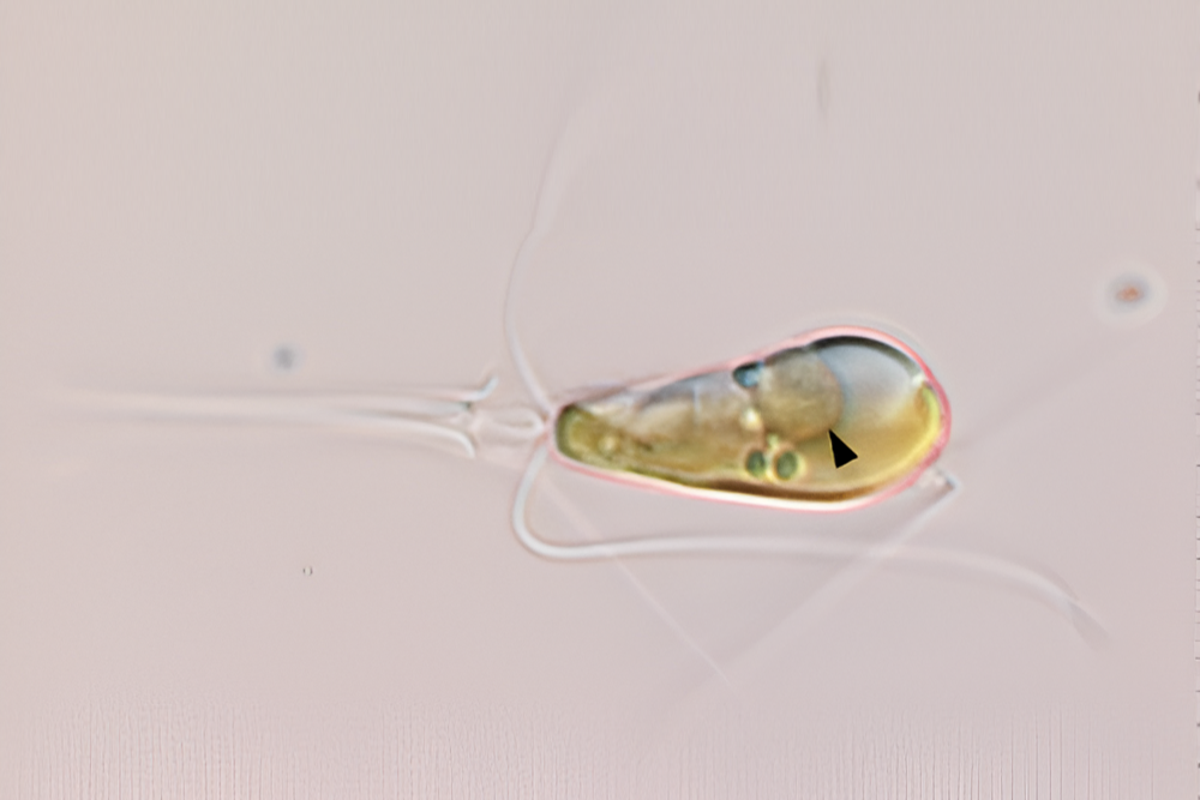
The Remarkable Fusion of Lifeforms: A Revolution in Evolution and Agriculture”.
In a remarkable evolutionary event, two lifeforms have merged to form a single organism through the process of primary endosymbiosis. This has only happened twice in the history of the…
2024 Grosvenor Teacher Fellowship: Arkansas Educator Jessica Culver Embarks on Global Adventure to Enhance Learning
Jessica Culver, a doctoral student in the College of Education and Health Professions Adult and Lifelong Learning program, has been selected to participate in the 2024 Grosvenor Teacher Fellowship program.…
The Future of Work in Texas: Navigating Shifts and Uncertainties in Key Industries
In the 1950s, agriculture work made up 10% of American workers, but today this number has decreased to less than 1%. This decline is posing challenges for small farms, particularly…
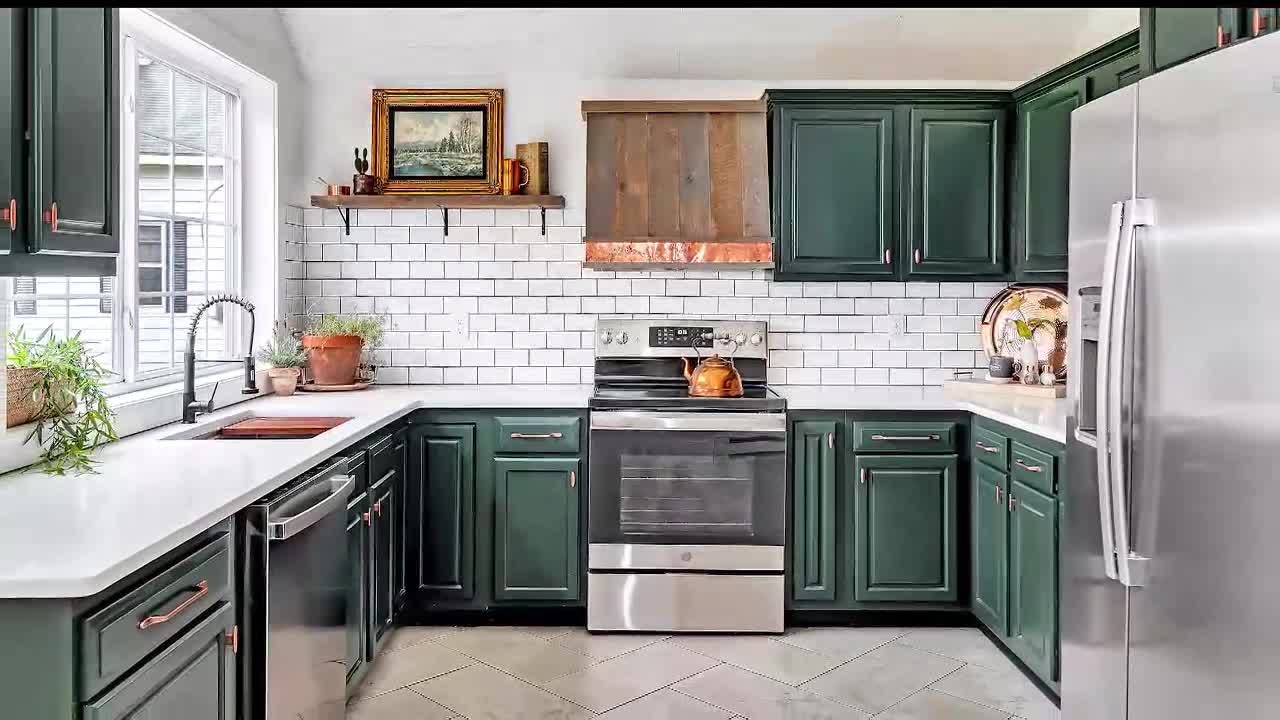
Revitalizing Kitchens on a Budget: The Rise of FunCycled in Wynantskill
FunCycled, a local family-owned business in Wynantskill, started out as a flipping company in 2021. They quickly expanded their offerings to include kitchen cabinet painting and interior design services. Their…
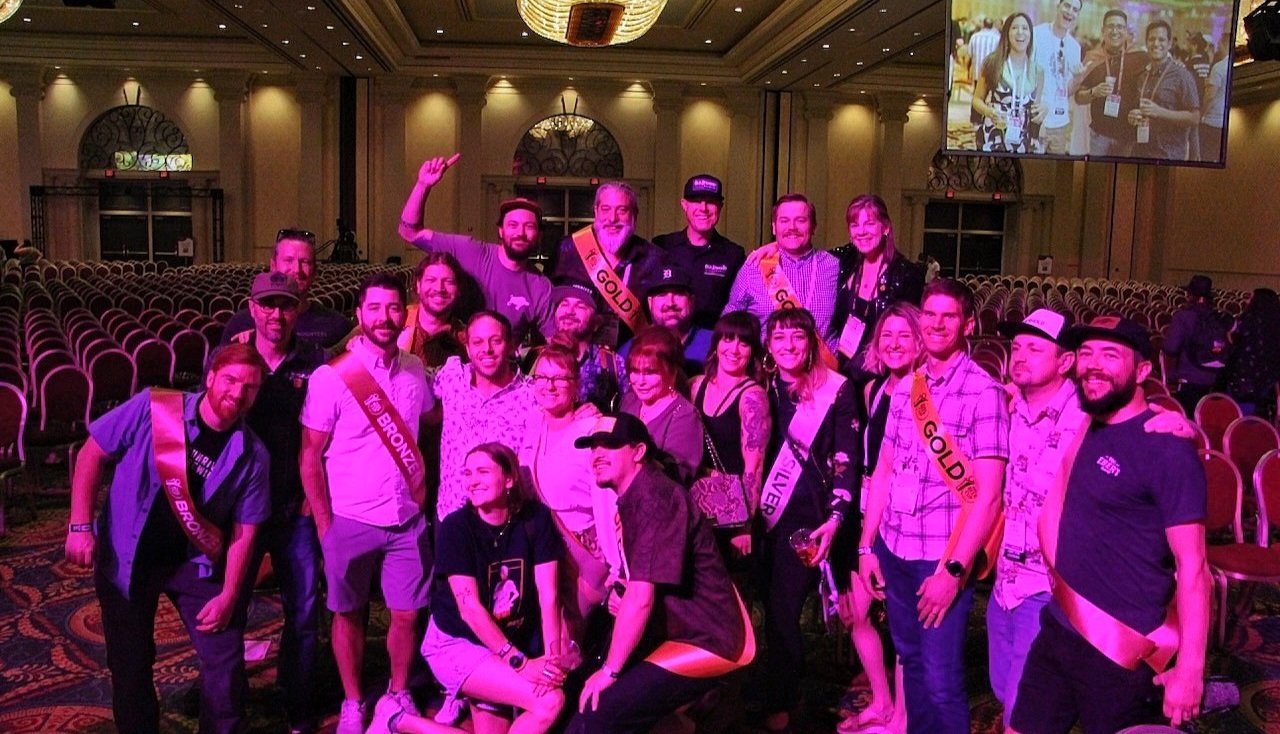
“Oregon Breweries Sweep the 2024 World Beer Cup with 29 Award-Winning Medals” – New School Beer + Cider
The 2024 World Beer Cup awards were held at The Venetian Las Vegas on April 24th, organized by the Brewers Association to celebrate brewing excellence on an international scale. Unlike…
Tinder introduces Share My Date feature to enhance safety in dating
Tinder, the popular dating app, is launching a new feature called “Share My Date” that allows users to share their date details with friends and family. This feature was created…
Sports Coverage on Bartlesville Radio
Sports Posted on Apr 24, 2024, at 7:08 AM, Bartlesville High baseball concluded its District season with a strong performance. The team secured a two-game sweep over Muskogee on Tuesday…
Bridging the Gap: Delta College’s Electron Microscopy Program Fuels Lucrative Career Paths for Diverse Aspiring Scientists
In the heart of Stockton, Delta College is training the next generation for lucrative careers in the world of science. During a free open house, the Eyes of Science display…
Rare E. Coli Outbreak: FSIS Warns Against Consuming Specific Ground Beef Products Manufactured by Greater Omaha Packing Co.
The Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) has issued a warning that some ground beef products may be contaminated with E. coli. Greater Omaha Packing Co., a meat processing company,…
Amazon Fined 10 Million Euros for Unfair Commercial Practices, Prompting Consumers to Buy Products They Don’t Need
The Amazon group’s two companies, Amazon Services Europe and Amazon EU, have been fined 10 million euros by the Antitrust for engaging in unfair commercial practices. Specifically, the investigation found…